Case Study
Mercury
Industrial automation platform, integrating edge computing with DLT and cybersecurity techniques
BACKGROUND
Current and future approaches to manufacturing require flexible, hyper-efficient systems so that manufacturers can support the transition from conventional to customized models. A flexible manufacturing system requires the ability to dynamically reconfigure, based on the needs of the environment, product, production or customer, with limited impact, capable of ensuring by-design security and trust over data and execution logic.
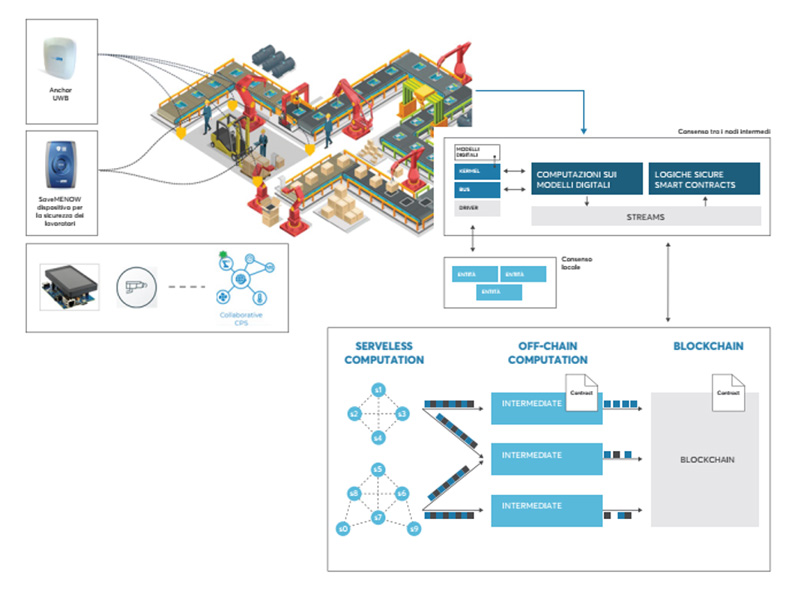
Decentralization, collaboration and secure logics were the elements at the base of the MERCURY project, which involved the design and implementation of an industrial automation platform that integrates Edge Computing approaches with basic techniques related to elements of Cybersecurity and Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT). This integration stands as an innovative and characterizing element of the proposed platform compared to similar implementations of industrial automation.
On the one hand, Edge Computing pushes the programming logic as low as possible in the automation pyramid, up to the field level, while increasing the distributed intelligence at the network nodes. On the other hand, programming according to the blockchain paradigm enables decentralization and parallelization of the logics themselves, as well as ensuring integrity, interoperability, and integration of the same programmed logics and the data produced at any level of the pyramid.
The project has identified models and technologies capable of supporting the execution of complex logic as close as possible to the data source and events also to enable the design of solutions consisting of communities of machines and collaborative sensors. Data automation and analysis processes have been implemented in the form of "Smart Contracts", i.e. decentralized blockchain-based programs that are dynamically configurable, securely stored and executable in a distributed fashion. Properties these can add integrity, flexibility and scalability to factory automation processes along the entire supply chain (i.e. from design to industrial product distribution).
The results have been supported by the definition of MCHAIN, the first blockchain platform in the Marche region available in the HD3FLab Laboratory and that intends to be characterized as a node compatible with the IBSI/EBSI (European Blockchain Service Infrastructure) initiative.
The technologies developed in a first phase of research and development have then been implemented in three different use cases at companies in the area.
DEVELOPMENT, INTEGRATION AND VALIDATION IN REAL APPLICATIONS
As a final result, the project has created industrial prototypes with a high degree of flexibility, which have highlighted the impact of the techniques studied in the previous OR. Following are the main outputs.
Use case DAPPS
(SMART CONTRACTS) ON EDGE COMPUTING AND COLLABORATIVE SENSOR TECHNOLOGY
The use case involves smart-tracking within a 4.0 production line characterized by the presence of (collaborative) robots, motion devices, operational systems and human operators. The use case is aimed at monitoring the position and movement of operators according to a paradigm that provides a trust on data from the field by default.
Use case Nuova Simonelli
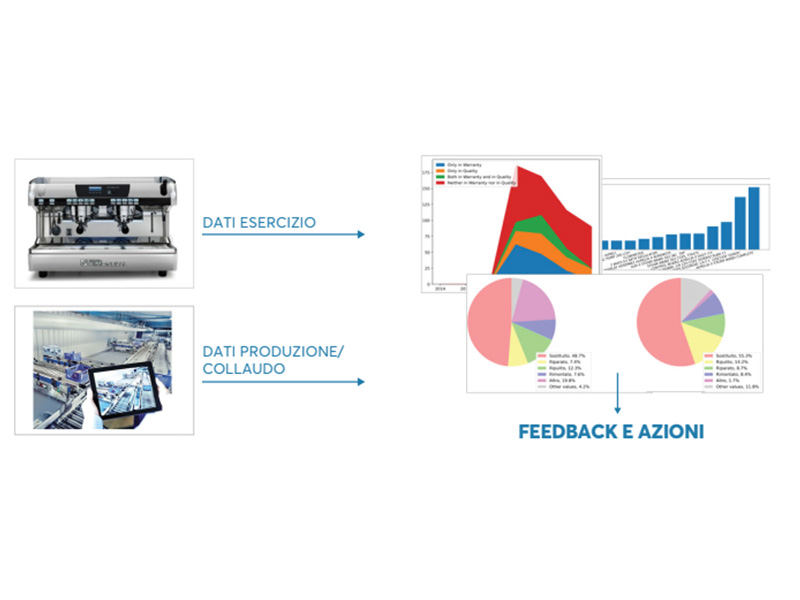
PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE
The use case involves the development of new "smart" models of use and maintenance of coffee machines (Nuova Simonelli). This approach allows a management of the operation (implementation of actions to restore and / or correction of operating modes) even remotely because the machines are constantly under control.
Use case Elica
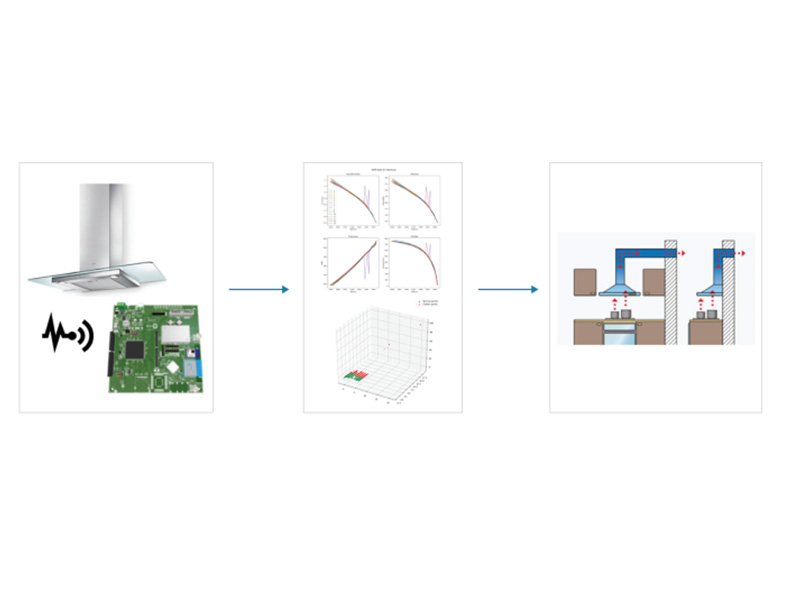
ADAPTIVE INSTALLATION
The use case foresees the identification of sensors and parameters to monitor the operation of the product (kitchen hoods by Elica) in the user in order to assess the correctness of installation, use and routine maintenance. In addition, the approach can provide suggestions to the user or automatically modify the product variables that can be controlled remotely.